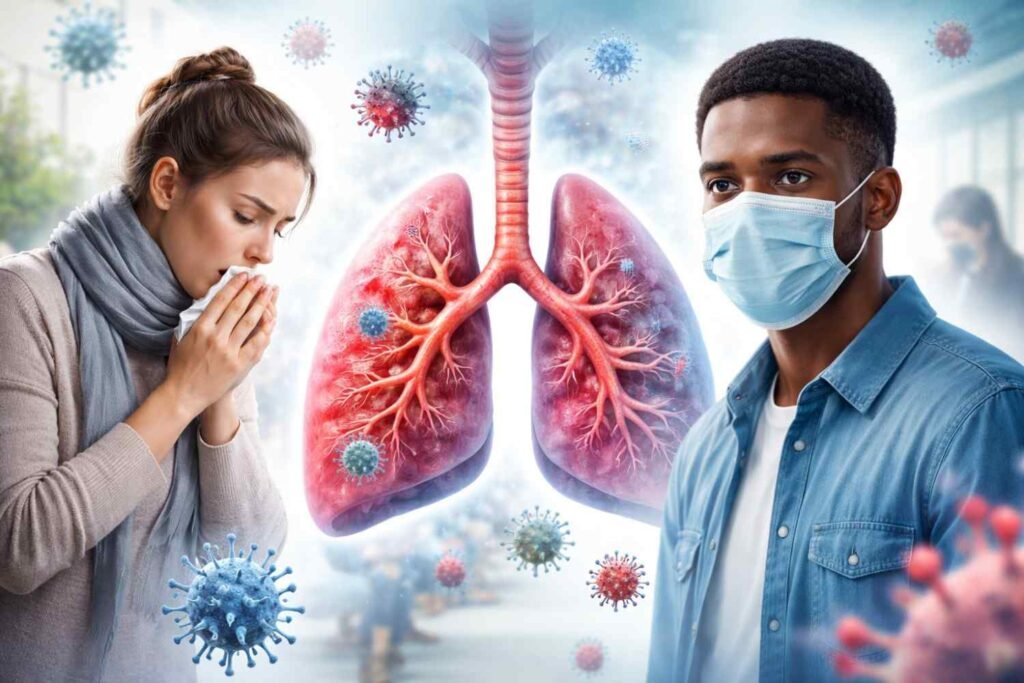
Have you ever wondered if being around someone who has a cough can cause you to have bronchitis? You’re not by yourself! Knowing how bronchitis spreads is crucial, whether you’re concerned about getting sick or infecting others. In actuality, it depends on the kind of bronchitis you have.
In this blog, I’ll break down the difference between acute and chronic bronchitis, when it’s contagious, and the simple steps you can take to protect yourself and others.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis refers to inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. When these tubes are irritated, they produce mucus, causing coughing, difficulty breathing, and chest discomfort. There are two main types of bronchitis:
Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is often caused by a viral infection, such as the viruses responsible for the common cold or flu. It is temporary and typically lasts for a few weeks. Acute bronchitis often begins after an upper respiratory infection and may cause a persistent cough, chest tightness, and wheezing.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition, often linked to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It is caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke, air pollution, or dust. Unlike acute bronchitis, chronic bronchitis is not contagious and is characterized by persistent coughing and mucus production.
Is Bronchitis Contagious?

The answer to “Is bronchitis contagious?” depends on the type of bronchitis you have.
Acute Bronchitis: Yes, It Is Contagious
Acute bronchitis is caused by viral infections, which means it is contagious. The virus spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or even talks. The virus can also spread via contaminated surfaces that are touched by an infected person.
Contagious Period:
Acute bronchitis is contagious for a few days to one week. If it’s bacterial, the contagious period usually ends after 24 hours of starting antibiotics.
Chronic Bronchitis: Not Contagious
On the other hand, chronic bronchitis is not contagious. It results from long-term exposure to irritants like tobacco smoke, air pollution, and dust, rather than from a viral or bacterial infection. Because it is a long-term lung condition, it cannot be passed to others.
Now that we’ve introduced the question, is bronchitis contagious? Let’s dive into how the virus spreads and what factors determine if you’re at risk.
How Does Bronchitis Spread?
Since acute bronchitis is often caused by a viral infection, it spreads in much the same way as a cold or flu:
Airborne Transmission
- Coughing, sneezing, or talking can release tiny droplets containing the virus into the air. These droplets can land on someone else, causing them to become infected.
Surface Contamination
- The virus can also survive on surfaces like doorknobs, phones, or countertops. If you touch a contaminated surface and then touch your face, mouth, or eyes, you may introduce the virus into your body.
When Are You Contagious with Bronchitis?
If you have acute bronchitis, you are generally contagious for as long as you have symptoms, especially a cough. Most people are contagious for about 3 to 7 days but may still spread the virus even after their symptoms start improving.
Chronic bronchitis, however, is not contagious because it is a result of long-term damage to the lungs rather than an infection.
How to Prevent the Spread of Bronchitis
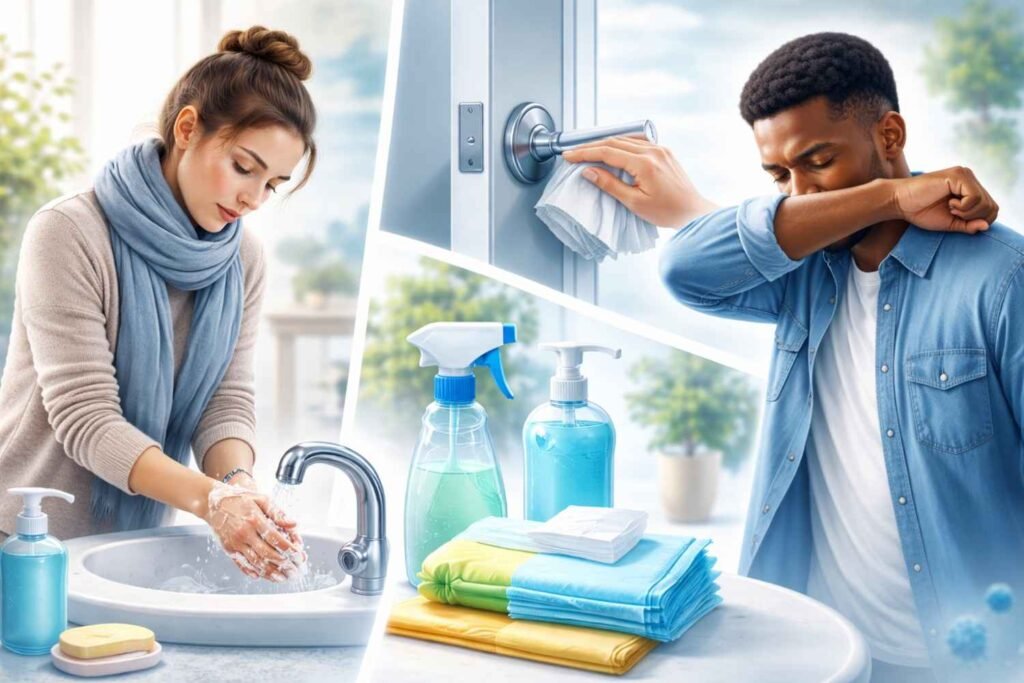

1. Good Hygiene Practices
To reduce the spread of viruses that cause bronchitis:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces such as doorknobs, phones, and light switches.
2. Stay Home When Sick
If you have acute bronchitis, it’s best to stay home from work or school to avoid spreading the virus to others. Resting will also help you recover more quickly.
3. Get Vaccinated
Keep up to date on flu, COVID-19, and RSV vaccinations to reduce the risk of viral infections that can lead to bronchitis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is bronchitis contagious in the early stages?
Yes, acute bronchitis is most contagious during the early stages, especially when you’re coughing, sneezing, or dealing with a runny nose.
2. How can I prevent bronchitis?
To prevent bronchitis, practice good hygiene, avoid smoking, and get vaccinated. Avoiding exposure to irritants and viruses will also help reduce your risk of developing bronchitis.
3. How long does acute bronchitis last?
Acute bronchitis typically lasts between 3 to 7 days, but the cough can linger for up to 3 weeks after other symptoms subside.
4, Can chronic bronchitis cause a contagious infection?
No, chronic bronchitis is not contagious. It is a long-term condition caused by repeated exposure to lung irritants, not by a viral or bacterial infection.
Protecting Yourself and Others from Bronchitis
The response varies depending on the type of bronchitis and contagion. Viral infections that cause acute bronchitis can spread through contaminated surfaces or droplets.
On the other hand, chronic bronchitis is caused by long-term lung damage and is not communicable. You can shield yourself and others against acute bronchitis and its spread by maintaining proper cleanliness, keeping at home while ill, and taking precautions.